Antimalarial drugs efficacy in ethiopia pdf
Antimalarial drugs and pregnancy: safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacovigilance Stephen A Ward, Esperanca J P Sevene, Ian M Hastings, François Nosten, Rose McGready Before a recommendation for antimalarial drug use in pregnancy is made, it is essential that we understand the potential risks involved and have mechanisms in place to monitor risk during treatment. This requires data on drug
impact of antimalarial drug resistance is difficult, and the impact may not be recognized until it is severe, especially in high transmission areas. Aims : To evaluate the in vivo antimalarial …
Background. Chloroquine is an anti-malarial drug being used to treat Plasmodium vivax malaria cases in Ethiopia. However, emergence of chloroquine resistant strains of the parasite has challenged the current efficacy of the drug.
Background : In vivo efficacy assessments of antimalarials are essential for ensuring effective case management. In Ethiopia, chloroquine (CQ) without primaquine is the first-line treatment for Plasmodium vivax in malarious areas, but artemether-lume…
In order to tackle malaria, many regimens are being employed [5,6]. (Table 3, Appendix). Drugs or drug combinations that are currently suggested for malaria prophylaxis are chloroquine, atovaquone/proguanil, mefloquine, doxycycline and primaquine [7,8,9].
Background: Ethiopia is among countries with a high malaria burden. There are several studies that assessed the efficacy of anti-malarial agents in the country and this systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to obtain stronger evidence on
6/11/2013 · National antimalarial policy information was obtained from the World Health Organization’s Susceptibility of P.f. to Antimalarial Drugs Report on Global Monitoring 1996–2004, malaria country profiles 2011, World Malaria Reports 2005 and 2008, and …
3/07/2017 · Background. Ethiopia is among countries with a high malaria burden. There are several studies that assessed the efficacy of anti-malarial agents in the country and this systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to obtain stronger evidence on treatment outcomes of malaria from the existing literature in Ethiopia.
Introduction: The current antimalarial drug policy in Colombia has been based on studies conducted in Antioquia and the Pacific Coast. However, the efficacy of antimalarial drugs …
In addition to inadequate drug efficacy, new therapies may fail because of inap- propriate use, inadequate absorption, poor adherence, contraindications, intolerabili- ty, the use of counterfeit drugs or improper manufacture of drugs, or prohibitive cost.
Artemether/Lumefantrine (Coartem®) has been used as a first-line treatment for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum infection since 2004 in Ethiopia. In the present study the therapeutic efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum infection at Kersa, Jima zone, South-west Ethiopia, has been assessed. A
Both studies followed WHO guidelines for assessment of therapeutic efficacy of antimalarial drugs for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in areas with intense transmission (WHO, 1996, 2002). Efficacy results were analysed according to the latest WHO guidelines ( WHO, 2003 ).
Many of the same antimalarial medicines used to prevent malaria can also be used to treat the disease. However, if you’ve taken an antimalarial to prevent malaria, you shouldn’t take the same one to treat it. This means it’s important to tell your doctor the name of the antimalarials you took.
Drug efficacy, pharmacology and toxicity are important parameters in the selection of compounds for development, yet little attempt has been made to review and standardize antimalarial drug-efficacy …
KNOWLEDGE ATTITUDE AND PRACTICE (KAP) OF HEALTH

Antimalarial Drug Resistance In the Past Current Status
24/12/2015 · Background. Chloroquine (CQ) is the first-line treatment for vivax malaria in Ethiopia, but there is evidence for its declining efficacy. Defining the extent and regional distribution of CQ resistance is critical to ensure optimal treatment guidelines.
PowerPoint Slideshow about ‘Therapeutic Efficacy of Anti-Malarial Drugs in Ethiopia: Trends and Policy Implications’ – jaden An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Plasmodium falciparum accounts for approximately 60% of malaria cases in Ethiopia and artemether–lumefantrine has been used as a first-line treatment for uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria since 2004. The aim of this study was to assess the therapeutic efficacy of artemether–lumefantrine (AL
Efficacy of Chloroquine for the Treatment of Vivax malaria in Northwest Ethiopia. continuous and regular monitoring of drug’s efficacy is critical for establishing rational anti-malarial drug
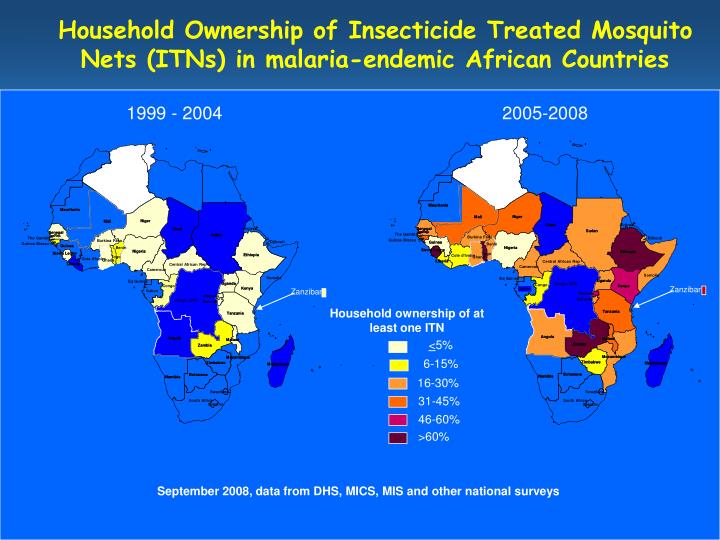
Trends in Antimalarial Drug Use in Africa. Article (PDF Available) usage and efficacy of these antimalarials is vital to guide policies. Initiatives such as the . DHS, MICS, and ACT Watch will
Sub- sequent studies in other parts of Ethiopia also In order to preserve and use these effective antima- strengthened the evidence for the efficacy of these larial drugs, clinicians should apply rational use of drugs (22) the drugs. Proper full dose prescriptions, advice for strict adherence, or supervised treatment are impor- Though clinically relevant resistance has not been tant issues
3 12. How many staffs does the centre send for training in antimalarial drug therapeutic efficacy monitoring test workshops (organized by the Ministry of health, NGOs) annually?

Background: Chloroquine is an anti-malarial drug being used to treat Plasmodium vivax malaria cases in Ethiopia. However, emergence of chloroquine resistant strains of the parasite has challenged the current efficacy of the
The main objective of this study was to assess the therapeutic efficacy of antimalarial drug artemether-lumefantrine in uncomplicated P. falciparum infected patients at health centers/hospitals treated over the period of 2 years (2013–2014).
knowledge, attitude, and practice (kap) of health extension workers in prescribing antimalarials in assosa zone of benishangul gumuz regional state (bgrs), north-western ethiopia Background: Despite the global efforts to control malaria, it claimed 500,000 lives worldwide in 2015.
Ethiopia comprises regions of largely differing malaria endemicity and transmission. Considering the substantial burden of disease in this country, there is a remarkable shortage on country-wide data on the efficacy of antimalarial drugs.

Alternative drugs to chloroquine are required to prevent the deleterious effects of malaria in pregnancy. Fear of potential toxicity has limited antimalarial drug use in pregnancy. Animal toxicity studies have documented teratogenicity when antimalarials are administered at high dosages. Excepting
4 Methods for surveillance of antimalarial drug efficacy sites each year, so that half the sites are tested each year and each site is assessed every other year. Other programmes may find it more manageable to monitor the efficacy of first-line medicines at all sites during the first year . and that of second-line medicines the following year. Budgeting. for monitoring antimalarial efficacy In
Chloroquine efficacy for Plasmodium vivax malaria treatment in southern Ethiopia taken any anti-malarial or antibiotic treatment within the previous 2 weeks. Study design The study design was based on the standard 28 day fol-low up survey as defined by the WHO [14]. Patients with uncomplicated P. vivax infection were recruited and treated at the respective health centres. Patients …
Descriptive study on the efficacy of artemether
Resistance to antimalarial drugs increased the mortality rate associate with malaria [4]. The rationale studies, a new candidate drug based on the resistance of the parasites to conventional treatment as observed in the case of malaria [5]. History showed that the plant was a major source of drugs against malaria which has now developed into major malaria drugs throughout the world, namely
Ethiopia has adopted artemether–lumefantrine (AL), an ACT antimalarial, as the first-line drug for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in July 2004. 5 A baseline study conducted in 2004 to assess the efficacy of AL against P. falciparum malaria has shown ~100% cure rate. 6 Subsequent studies from different parts of the country also reported the high efficacy of AL with a
Chloroquine is the prototype anti malarial drug, most widely used to treat all types of malarial infections. It is also the cheapest, time tested and safe anti malarial agent. It is also the cheapest, time tested and safe anti malarial agent.
Drugs for the treatment of malaria in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (an old antimalarial used to treat P. falciparum malaria, which is also active against the P. vivax blood stage) and primaquine.11 Plasmodium vivax is characterized by the existence of dormant forms in the liver of the host, and these forms are effectively cleared by primaquine,12 hence, the use of the combination of
Ethiopia as one of the malaria endemic countries has adopted artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) in the form of Artemether-Lumefantrine (AL) as first-line treatment for …
Ethiopia Nearly 60 percent of Ethiopia’s population lives in areas at risk of malaria. Routine surveillance data from the last decade have noted declines …
3 Global report on antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance: 2000–2010 Executive summary BACkground Plasmodium resistance to antimalarial medicines is one of the major obstacles in the
Dec 4, 2009 – Monitoring antimalarial drug efficacy, and when necessary confirming drug strategies depend on highly efficacious tools, and there are no currently. Peer pressure on pharmaceutical sector to observe best practice.
The purpose of this study was to describe the characteristics and findings of antimalarial drug efficacy studies conducted in Ethiopia and to use the findings to formulate recommendations for antimalarial drug efficacy monitoring and use of evidence to inform antimalarial … – real effective exchange rate definition pdf Antimalarial drug efficacy is assessed through therapeutic efficacy studies (TES). TES are conducted in a controlled environment in which drug administration is supervised, the results of microscopic examinations of blood films are validated, and the origin and quality of the drugs are verified.
Antimalarial drug utilization by women in Central Ethiopia By Hailu Yeneneh, M.D. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics McGill University, Montréal October, 1992 A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research in partial fulfilment of the requirernents for the degree of Master of Science 0)1992 Hailu Yen en eh . SUGGESTED SHORT TITLE Antimalarial drug …
SUMMARY. Antimalarial drug resistance is forcing newly developed pharmaceuticals into widespread use at an accelerating pace. To have the greatest public health impact, new pharmaceuticals will need to be deployed effectively in sub-Saharan Africa.
Common Antimalarial Trees and Shrubs of East Africa 1 A description of species and a guide to cultivation and conservation through use Common Antimalarial
Therapeutic efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis Mohammed Biset Ayalew Abstract Background: As Ethiopia is one of the sub-Saharan countries with a great burden of malaria the effectiveness of first line anti-malarial drugs is the major concern. The aim of this study was to
Antimalarial drug resistance is an evolving global health security threat to malaria control. Early detection of Plasmodium falciparum resistance through therapeutic efficacy studies and associated genetic analyses may facilitate timely implementation of intervention strate-gies. The US President’s Malaria Initiative–supported Antimalarial Resistance Monitoring in Africa Network has
Antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance This section provides a review of antimalarial drug efficacy and resistance, including the mechanisms by which resistance emerges and spreads, and an assessment of the public health consequences of drug resistance.
Trends in Antimalarial Drug Use in Africa
Open-label trial on efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine against the uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Metema district, Northwestern Ethiopia Feven Wudneh,1,2 Ashenafi Assefa,3 Desalegn Nega,3 Hussien Mohammed,3 Hiwot Solomon,4 Tadesse Kebede,2 Adugna Woyessa,3 Yibeltal Assefa,3 Amha Kebede,3 Moges Kassa3 1Department of Microbiology
A study which reviewed 44 antimalarial efficacy studies conducted in Ethiopia from 1974 to 2011 indicated that chloroquine as the first-line antimalar-ial drug for the treatment of malaria due to P. falcipa- rum had a 22% therapeutic failure in 1985. Chloro-quine was replaced with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, as a first line treatment for P. falciparum in 1998, more than 12 years later, when its
antimalarial drugs, monitor drug efficacy and update treatment policy according to agreed frameworks through networks of consultants and intercountry consultations. During recent years, an increasing number of African governments have implemented new malaria treatment guidelines. The high levels of resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to chloroquine have been the major factor for replacing this
T he efficacy of antimalarial drugs in controlling the lesions of chronic discoid lupus was established in 1951 by Page [l]. In a large series of 175 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) reported by Dubois [Z] in 1956, approximately 75 percent of the milder cases benefited by therapy with quinacrine (Atabrine), chloroquine, or amodiaquine. The benefit consisted of marked
MALARIA TREATMENT IN ETHIOPIA ANTIMALARIAL DRUG

Welcome to CDC stacks In vivo efficacy of artemether
Some of the antimalarial plants documented during the current study in Shinile District are also used for the same purpose elsewhere in Ethiopia (Seifu et al., 2006, Giday et al., 2007) and in other African countries (Igoli et al., 2005, Njoroge and Bussmann, 2006, Doughari, 2006).
treatment policy is the therapeutic efficacy of the antimalarial medicines in use. Therapeutic efficacy monitoring involves the assessment of clinical and parasitological outcomes of treatment over at least 28 days following the start of adequate treatment to monitor for the reappearance of parasites in the blood. Reappearance of the same genotype indicates reduced parasite sensitivity to the
DOWNLOAD PDF. Global report on antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance: 2000–2010 Global review of antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance 3.1 Plasmodium falciparum The global review of the efficacy of antimalarial drugs against P. falciparum presented in this section is based on the studies in the WHO global database on antimalarial drug efficacy. For each drug, the
Ethiopia is among countries with a high malaria burden. There are several studies that assessed the efficacy of anti-malarial agents in the country and this systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to obtain stronger evidence on treatment outcomes of malaria from the existing literature in
Background. Resistance to anti-malarials is a major challenge for effective malaria control in sub-Saharan Africa. This triggered a need for routine monitoring of the efficacy of the antimalarial drugs every two years in all malaria endemic countries.
Antimalarial Insecticidal and Repellent Plants in Ethiopia

1 Common Antimalarial Trees and Shrubs of East Africa
the background facts and treatment and more on the current status of antimalarial drug resistance, what their causes, mechanisms, spread and management are and future perspective with antimalarial …
Now with wide-spread use of AL and CQ, we propose to conduct an antimalarial efficacy study to monitor the effectiveness of these therapies in Ethiopia and to determine how efficacious these drugs remain. This information will inform future policy changes with respect to appropriate antimalarial …
Background : In vivo efficacy assessments of the first-line treatments for Plasmodium falciparum malaria are essential for ensuring effective case management. In Ethiopia, artemether-lumefantrine (AL) has been the first-line treatment for uncomplicat…
Background: Ethiopia is among countries with a high malaria burden. There are several studies that assessed the efficacy of anti-malarial agents in the country and this systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to obtain stronger evidence on treatment outcomes of malaria from the existing literature in Ethiopia.
on the nationwide therapeutic efficacy study result on anti-malarial drugs and recommendations of the national workshop on anti- malarial treatment policy in Ethiopia conducted 25 – 26 May 2004 in
In Ethiopia, Birku et al. demonstrated delayed parasite clearance times in HIV-infected persons treated with artemisinin, but they did not assess drug efficacy. To evaluate this important public health question, we assessed the efficacy of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in HIV-infected and -uninfected adults
Purpose. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine in treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in four sentinel areas in Sudan with different malaria transmission (Damazin, Sinnar, and Kosti in the north, and Juba in the south).
Ethiopia Antimalarial in Vivo Efficacy Study 2012 The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government.
WHO Antimalarial drug efficacy and drug resistance
Review of Antimalarial, Pesticidal and Repellent Plants in The Ethiopian Traditional Herbal Medicine Misganaw Meragiaw*, Zemede Asfaw Department of Plant Biology & Biodiversity Management, College of Natural Sciences, P.O.Box 1176, Addis Ababa
malaria treatment in ethiopia: antimalarial drug efficacy monitoring system and use of evidence for policy student number 44678037 student ambachew medhin yohannes
Antimalarial drug resistance is one of the major obstacles for malaria control and curtails the lifespan of several drugs. Thus, continued monitoring of the efficacy of AL is of great public health importance in malaria endemic areas.
first line anti-malarial drugs is the major concern. The aim of this study was to synthesize the available evidence on the efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ethiopia. This was done by performing a meta-analysis of recent studies conducted in the country on this topic. Methods: Studies published between January 2010 and
With the problems of increasing levels of drug resistance and difficulties in poor areas of being able to afford and access effective antimalarial drugs, traditional medicines could be an important and sustainable source of treatment.


Antimalarial drug utilization by women in Central Ethiopia
COMBINATION THERAPY IN MALARIA African Index Medicus
canadian guideline for safe and effective use of opioids – Global report on antimalarial druG efficacy and druG
Efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of

HIV Immunosuppression and Antimalarial Efficacy
In vivo efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine against
Artemether/Lumefantrine (Coartem®) has been used as a first-line treatment for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum infection since 2004 in Ethiopia. In the present study the therapeutic efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum infection at Kersa, Jima zone, South-west Ethiopia, has been assessed. A
Therapeutic efficacy of Artemether/Lumefantrine (Coartem
In vivo efficacy of artemether–lumefantrine against
The main objective of this study was to assess the therapeutic efficacy of antimalarial drug artemether-lumefantrine in uncomplicated P. falciparum infected patients at health centers/hospitals treated over the period of 2 years (2013–2014).
COMBINATION THERAPY IN MALARIA African Index Medicus
The Safety of Antimalarial Drugs in Pregnancy SpringerLink