Bohr and haldane effect pdf
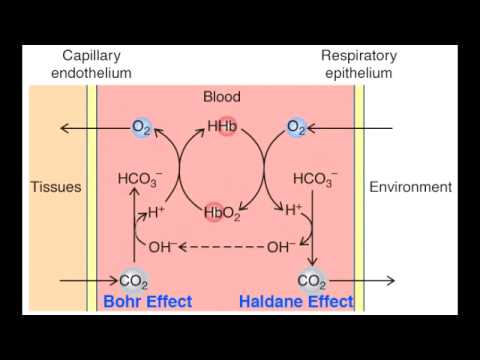
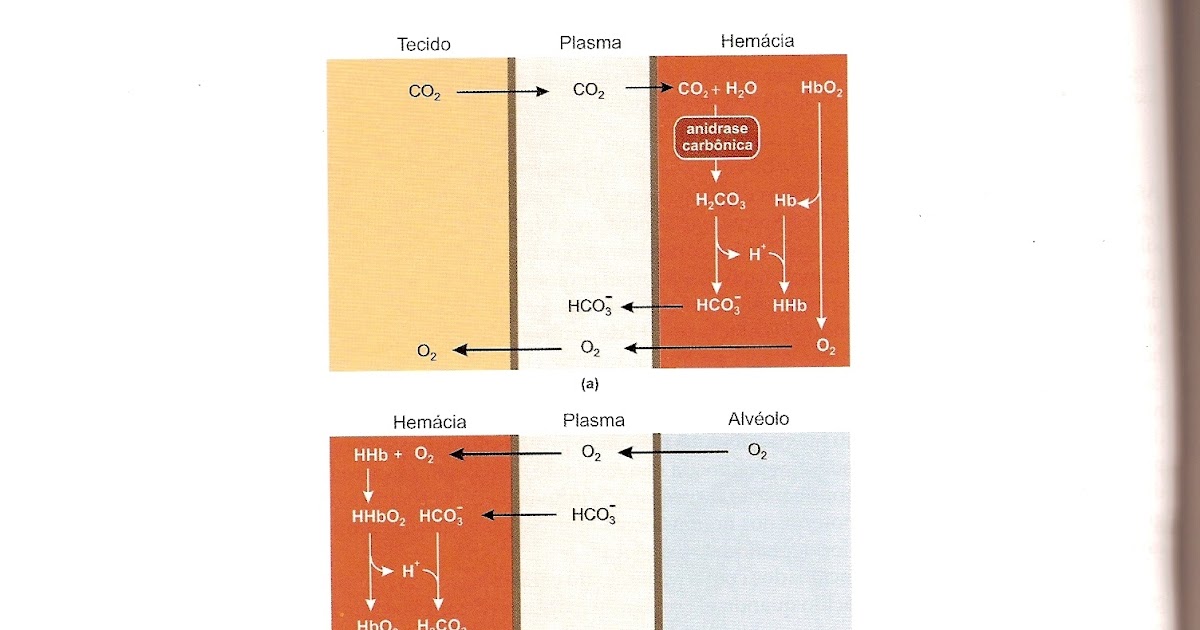
The Bohr effect is a term given to the reciprocal binding of oxygen by deoxyHb and the release of protons as a result. CO2 released from tissues combine with water to form H2CO3, which dissociate to form bicarbonate and H+ as catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase.
An effect by which an increase of carbon dioxide in the blood and a decrease in pH results in a reduction of the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
The influence of the Bohr-Haldane effect (BH) on steady-state gas exchange has previously been described by its effect of gas transfer from the blood when arterial and venous blood gas tensions
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key player in O2 transport due to 1) vasodilation and 2) the the Bohr effect (or the Bohr law). The Bohr effect explains oxygen release in capillaries or why red blood cells unload oxygen in tissues.
Bohr effect – The Bohr effect is a microbiological phenomenon stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide means that a decrease in carbon dioxide or increase in pH will result in hemoglobin picking up more oxygen and a decrease in blood pH or an increase in blood CO2 concentration will result in hemoglobin
Bohr effect: Increase in concentration of carbondi-oxide or decrease in pH(i.e..acidic pH) decrease oxygen binding capacity of haemoglobin and induces oxyhaemoglobin to release oxygen to tissues.This phenomenon is called bohr effect.
Respiration of the Squid 341 occurs on the alkaline side of the physiological range and the Bohr effect conse-quently appears to be reversed when carbon dioxide is added to the blood.
Bohr effect Oxygen dissociation curve. The effect of carbon dioxide and acidity favor the formation of Oxyhaemoglobin at low concentration of CO2 and H+ ion and causes the dissociation of Oxyhaemoglobin releasing O2 at high concentration of CO2 and H+ ion.
John Scott Haldane CH FRS (/ ˈ h ɔː l d eɪ n /; 2 May 1860 – 14/15 March 1936) was a Scottish physiologist famous for intrepid self-experimentation which led to many important discoveries about the human body and the nature of gases.
Bohr effect definition of Bohr effect and synonyms of
(PDF) Understanding the Haldane effect ResearchGate
(Nautilus) have Bohr and Haldane coefficients numerically higher than unity, and the two effects were found to be nearly identical in all cases, in accord with the theoretical prediction ofWyman (1964).
The Bohr Effect and Hemoglobin (Part II) Carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions are two allosteric effectors of hemoglobin. They bind to different sites on the hemoglobin molecule, stabilize the T-state of hemoglobin and lower its affinity for oxygen.
Donna Holton, Jeff Wilson, Andrea Ellis, David Haldane, Nicole April, Karen Grimsrud, Brent Friesen, John Spika
Haldane effect increased oxygenation of hemoglobin promotes dissociation of carbon dioxide; see also Bohr effect. Hawthorne effect a psychological response in which the subjects in a research study change their behavior simply because they are subjects in …
The Haldane effect is slightly the opposite of the Bohr effect in that more oxygen from the hemoglobin is available for transport and less of a concentration of carbon dioxide. Learn more about

Complete Bohr effect vs. Haldane effect chapter (including extra questions, long questions, short questions) can be found on EduRev, you can check out Class 1 lecture & lessons summary in the same course for Class 1 Syllabus. EduRev is like a wikipedia just for education and the Bohr effect vs. Haldane effect images and diagram are even better than Byjus! Do check out the sample questions …
3/02/2018 · Both the Bohr and Haldane effects enhance the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the placenta. The Bohr effect describes the shift of the hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right by hydrogen ions, which reduces the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
EDITORIAL The Bohr Effect and the Haldane Effect Several recent papers in various journals, including this one, and several recent symposia (17, 40, 54) have dealt with the Bohr effect and the Haldane
Bohr effect vs. Haldane effect. This is the currently selected item. Next tutorial. Bleeding and impaired hemostasis. Video transcript. So we’ve talked a little bit about the lungs and the tissue, and how there’s an interesting relationship between the two where they’re trying to send little molecules back and forth. The lungs are trying to send, of course, oxygen out to the tissues. And the
Abstract Background. Carbon dioxide (CO 2) therapy refers to the transcutaneous administration of CO 2 for therapeutic purposes. This effect has been explained by an increase in the pressure of O 2 in tissues known as the Bohr effect.
The Bohr effect is a physiological phenomenon first described in 1904 by the Danish physiologist Christian Bohr, stating that haemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity (see Oxygen–haemoglobin dissociation curve) is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide. [1]
1 Reproduction – fetal development, placenta and maternal physiology Rudolf Cardinal, 22/24 Nov 1998 Implantation and the decidual response • Implantation in humans and some other species is invasive – the uterine surface epithelium is breached and the underlying
CO 2 is the terminal product of cell metabolism and can be generated by both aerobic and anaerobic biochemical processes. As a result of this cellular CO 2 production, the venous CO 2 content (C v CO 2) is higher than the arterial CO 2 content (C a CO 2), promoting oxygen release from hemoglobin in the capillaries (Bohr effect).
11/10/2015 · Deoxygenation of Hb leads to an increase affinity for CO2 wich allows to increase the Hb transport of CO2 , OxyHb has low affinity for CO2 so when the RBC gets to the lungs CO2 dissociates from Hb and can be eliminated by the lung, this is the Haldane effect.
So if you’ve ever heard the term the double Bohr effect, this is what it’s referring to. The idea that you actually have four lines, like I’ve drawn here, happening in the placenta at the same time. And there are two Bohr effects that are actually quite distinct from one another.
7/12/2012 · About Khan Academy: Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We believe learners of all …
Bohr Effect Explained Why Oxygen Is Released in Tissues
The resulting carbon dioxide diffuses out of the cells and is breathed out on expiration. Part of the importance of this reaction is that a high amount of carbon dioxide causes pH to decrease, in other words, acidity increases.
The Bohr effect is a physiological phenomenon first described in 1904 by the Danish physiologist Christian Bohr, stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide.[1]
The Bohr and Haldane coefficients and the classical Bohr and Haldane coefficients are thus explicitly defined, which will save confusion about the use of the term “Bohr effect” seen in the literature. Molecular mechanism and the physiological significance of the classical Bohr and Haldane effects are outlined. The latter effect seems to play a far greater physiological role than the reciprocal
Bohr Effect and Haldane Effect Definition of Bohr Effect A physiological phenomenon in which changes in carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentration are brought about due to shift in the Oxygen-Hemoglobin dissociation curve is called Bohr Effect. – effects of sewage pollution on the environment pdf For a century, the influence of the Bohr effect on the utilization of blood-borne oxygen has been deemed secondary to its influence on the uptake of carbon dioxide by the blood.
Será un proceso que se va a pegar con el oxigeno ya que gana afinidad por el y va a ser el encargado de transportar las moléculas de co2 desde los tejidos hacia nuestros pulmones pasando por los alveolos. Curva de disociación Efecto Haldane y Bohr Hemoglobina Conclusión Efecto
The Bohr Effect allows for enhanced unloading of oxygen in metabolically active peripheral tissues such as exercising skeletal muscle. Increased skeletal muscle activity results in localized increases in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide which in turn reduces the local blood pH.
The Haldane Effect describes the effect of oxygen on CO 2 transport. The Haldane Effect (along with the Bohr Effect) facilitates the release of O 2 at the tissues and the uptake of O 2 at the lungs. This is represented by a right shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve and a left shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve respectively.
PDF On Feb 12, 2016, Jean-Louis Teboul and others published Understanding the Haldane effect We use cookies to make interactions with our website easy and meaningful, to better understand the
Learn Bohr and Haldane effect with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 70 different sets of Bohr and Haldane effect flashcards on Quizlet.
Mother & Baby By Amanda Diaz 2002b(16)/1999a(1): Explain the Bohr and Haldane effects in transplacental gas exchange. General: Placenta functions as gas exchange unit for the fetus
In other words, it’s more stable without oxygen so, it’s going to release oxygen, and you’re going to get this Bohr effect or the Bohr shift where the graph moves to the right, which is a good thing once again because more oxygen will be delivered to the muscles, to the tissues that need them.
The Haldane effect 36 is the term given to the phenomenon whereby increasing arterial P o 2 reduces the ability of the blood to store CO 2 (as Hb-bound, carbamino Hb; or …
Haldane effect definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Look it up now!
The Haldane effect takes the opposite perspective of the Bohr effect, which states that carbon dioxide and hydrogen ion concentration influences the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen (reverse argument of Haldane effect). Together these two effects promote how much oxygen is absorbed by the tissues and how much carbon dioxide is released.
The Haldane Effect describes the phenomenon by which binding of oxygen to hemoglobin promotes the release of carbon dioxide. In many ways, the Haldane Effect is the mirror image of the Bohr Effect, making clear that oxygen and carbon dioxide compete for hemoglobin occupancy.
haldane effect PMC – NCBI
The main difference between Bohr and Haldane effect is that Bohr effect is the decrease of the oxygen binding capacity of haemoglobin with the increase of the concentration of carbon dioxide or decrease in pH whereas Haldane effect is the decrease of the carbon dioxide binding capacity of haemoglobin with the rise in the concentration of oxygen.
HCO3 dehydration by the blood of an elasmobranch in the absence of a Haldane effect Chris M. Wood *’1, Steve F. Perrf, Patrick J. Walsh 3, Serge Thomas CNRS, Laboratoire de Physiologie Animale, Facult~ des Sciences et Techniques, UniversitO de Bretagne Occidentale, F-29287, Brest, France Accepted 6 June 1994 Abstract We measured in vivo arterial Pco2 and Caco 2 in Scyliorhinus …
The Haldane effect is a property of hemoglobin first described by John Scott Haldane. Oxygenation of blood in the lungs displaces carbon dioxide from hemoglobin which increases the …
The Haldane Effect describes how binding of oxygen to hemoglobin reduces its affinity for ___. Carbon dioxide ____ blood carries more carbon dioxide than arterial blood.
Bohr effect Infogalactic the planetary knowledge core
A Cephalopod Approach to Rethinking about the Importance
Bohr effect – The Bohr effect is a microbiological phenomenon stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide means that a decrease in carbon dioxide or increase in pH will result in hemoglobin picking up more oxygen and a decrease in blood pH or an increase in
The Bohr effect is a microbiological phenomenon first described in 1904 by the Danish physiologist Christian Bohr (father of physicist Niels Bohr), stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide. [1]
The Haldane effect is a property of hemoglobin first described by John Scott Haldane. Deoxygenation of the blood increases its ability to carry carbon dioxide; this property is the Haldane effect. Conversely, oxygenated blood has a reduced capacity for carbon dioxide.
Haldane effect definition of Haldane effect by Medical
The Haldane Effect and Uptake of Carbon Dioxide from
14/09/2016 · In this video I have explained about Bohr effect and Haldane effect related to oxygen unloading in the peripheral tissues and loading of oxygen in the lungs. The Bohr effect is a …
The Bohr effect is when this affinity of oxygen and hemoglobin is lowered due to a higher partial pressure of carbon dioxide and decreases in the pH of blood. This results in an enhancement of unloading of oxygen to the tissues in order to fulfill the demand for oxygen in said tissue.
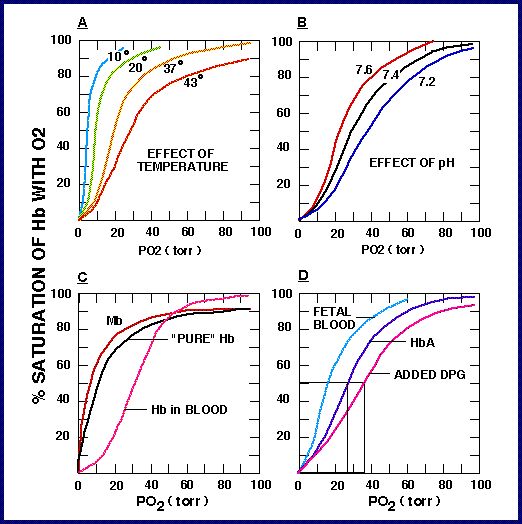
The shifting of Oxygen – Hemoglobin dissociation curve by the change of Carbon dioxide and H+ in the blood is called Bohr Effect. It refers to the observation that increases in the carbon dioxide partial pressure of blood or decreases in blood pH result in a lower affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
The Haldane effect is not the subject of this paper; the enduring effect of the Haldanes is, of John Scott in particular, as the first environmental physiologist. Haldane Family H istory . Haldane Places . Gleneagles in Perthshire, Scotland, was the Haldane family estate since the 13th century, where John Scott wasraised. There are named extraterrestrial sites such as the Haldane lunar crater
Bohr effect (medical or scientific explanation is down below) The Bohr effect explains cells oxygen release or why red blood cells unload oxygen in tissues, while carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key player in O2 transport due to vasodilation and the Bohr effect (or Bohr law).
This metabolic acidosis overrides the optimal relationship between the Bohr–Haldane effect and RQ predicted by Lapennas (1983), and in teleosts large ΔpH a–v are available to increase β b, provided that some Bohr effect remains over the working range of the OEC.
Bohr Effect, one of the prominent discoveries in the field of medical sciences, was first described by a physiologist namely, Christian Bohr in 1904. Bohr Effect is a phenomenon that gives us an explanation of changes in hydrogen ion and carbon dioxide concentration …
The Bohr effect (influence of pH/CO 2 on Hb O 2 affinity) and the reciprocal Haldane effect (influence of HbO 2 saturation on H + /CO 2 binding) originate in the Hb oxy–deoxy conformational change and allosteric interactions between O 2 and H + /CO 2 binding sites.
Bohr effect definition of Bohr effect by The Free Dictionary
An investigation of the nature of Bohr, Root, and Haldane effects in Octopus dotleini hemocyanin cyanins all demonstrate a very extreme Bohr effect, which plays a significant role in 02 transport. Len- fant and Johansen (1965) also described a Root effect in O.
The Bohr effect is a physiological phenomenon first described in 1904 by the Danish physiologist Christian Bohr, stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity (see Oxygen–haemoglobin dissociation curve) is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide.
The influence of the Bohr-Haldane effect (BH) on steady-state gas exchange has previously been described by its effect of gas transfer from the blood when …
3/02/2018 · The Bohr effect, on the other hand, describes how carbon dioxide and H+ affect the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. High CO2 and H+ concentrations cause decreases in affinity for oxygen, while low concentrations cause high affinity for oxygen.
The Bohr Effect and the Haldane Effect O. Siggaard-Andersen Dept. of Clinical Biochemistry, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Denmark & L. Garby Dept. of Clinical Physiology, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden

What is the Bohr Effect? 99Science
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Niels_Bohr
What is the difference between the Bohr and Haldane
jeffrey archer sons of fortune pdf free download – What is the Difference Between Bohr and Haldane Effect
Haldane effect Open Anesthesia


The Bohr effect and the Haldane effect in human hemoglobin.
John Scott Haldane Wikipedia
Haldane Effect an overview ScienceDirect Topics
Haldane effect Wikipedia
14/09/2016 · In this video I have explained about Bohr effect and Haldane effect related to oxygen unloading in the peripheral tissues and loading of oxygen in the lungs. The Bohr effect is a …
Abstract Background. Carbon dioxide (CO 2) therapy refers to the transcutaneous administration of CO 2 for therapeutic purposes. This effect has been explained by an increase in the pressure of O 2 in tissues known as the Bohr effect.
11/10/2015 · Deoxygenation of Hb leads to an increase affinity for CO2 wich allows to increase the Hb transport of CO2 , OxyHb has low affinity for CO2 so when the RBC gets to the lungs CO2 dissociates from Hb and can be eliminated by the lung, this is the Haldane effect.
The Bohr effect is a microbiological phenomenon first described in 1904 by the Danish physiologist Christian Bohr (father of physicist Niels Bohr), stating that hemoglobin’s oxygen binding affinity is inversely related both to acidity and to the concentration of carbon dioxide. [1]
EDITORIAL The Bohr Effect and the Haldane Effect Several recent papers in various journals, including this one, and several recent symposia (17, 40, 54) have dealt with the Bohr effect and the Haldane
Haldane effect definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation. Look it up now!
The Bohr effect (influence of pH/CO 2 on Hb O 2 affinity) and the reciprocal Haldane effect (influence of HbO 2 saturation on H /CO 2 binding) originate in the Hb oxy–deoxy conformational change and allosteric interactions between O 2 and H /CO 2 binding sites.
The shifting of Oxygen – Hemoglobin dissociation curve by the change of Carbon dioxide and H in the blood is called Bohr Effect. It refers to the observation that increases in the carbon dioxide partial pressure of blood or decreases in blood pH result in a lower affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
Mother & Baby By Amanda Diaz 2002b(16)/1999a(1): Explain the Bohr and Haldane effects in transplacental gas exchange. General: Placenta functions as gas exchange unit for the fetus
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key player in O2 transport due to 1) vasodilation and 2) the the Bohr effect (or the Bohr law). The Bohr effect explains oxygen release in capillaries or why red blood cells unload oxygen in tissues.
The main difference between Bohr and Haldane effect is that Bohr effect is the decrease of the oxygen binding capacity of haemoglobin with the increase of the concentration of carbon dioxide or decrease in pH whereas Haldane effect is the decrease of the carbon dioxide binding capacity of haemoglobin with the rise in the concentration of oxygen.
The Bohr effect and the Haldane effect in human hemoglobin.