Effect of pressure on melting point of ice pdf
Cooling of sea-water to its pressure melting point by melting of ice at depth has two important results. The outflow of cold, dense Ice Shelf Water, produced by this mechanism, is a major source
b) The melting point increases when the air pressure increases c) The melting point decreases When the air pressure increases The boiling point has inverse relation with vapor pressure of the liquid and positive relation with atmosphere (air) pressure.
1/02/2017 · The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure. For example: The melting point of ice at 1 atmosphere of pressure …
14 Masato Kida, Yusuke Jin, Hideo Narita, Jiro Nagao, Effective control of gas hydrate dissociation above the melting point of ice, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011, 13, 41, 18481CrossRef
the pressure-melting explanation on the basis of calcula- tions of the pressure required to melt ice at low tempera- tures and on the basis of the phase diagram, which shows
To determine the effects of different substances such as road salt, calcium chloride, sand, kitty litter, calcium magnesium acetate and Safe Paw (a commercial eco-friendly product) on melting ice while protecting the lawn.
THE EFFECT OF SURFACE ON MELTING POINT* Howard Reiss Columbia University, N. Y. and Irwin B. Wilson College of the City of New York Received August 16, 1948 Very few quantitative investigations of the effect of surface upon fusion have been carried out.
The Melting Point of Ice When ice melts, the resulting mixture of ice and water has a temperature of exactly 0.00 °C under normal atmospheric pressure This is a fundamental, physical property of water We call the temperature equilibration of ice and
Freezing and Melting of Water The cooling and warming behavior of water is investigated. With the use of technology, water temperature data is collected, graphed and analyzed. The freezing and melting points of water are determined and compared. Hypothesis The freezing and melting points of a substance may be determined by observing the warming and cooling behavior of that substance. …
pressure on its lower surface to lower the melting point of the ice at its base, melting the ice and allowing the glacier to slide over the liquid. Under the right …
31/12/2015 · The market sales of premium ice cream have paralleled the growth in consumer desire for rich flavor and taste. Storage temperature is a major consideration in preserving the quality attributes of premium ice cream products for both the manufacturer and …
Causes and Effects of Melting Ice — 4 12. Re-measure the sea level and label it as New Sea Level 1 (NSL1) on your plastic container. NOTE: Observe the layer of colored water in the container after the ice …
With a pressure change apply Le Châtelier’s principle – “If a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in pressure . . . . . . . then the equilibrium shifts in such a way so as to undo the effect …
The added pressure from the weight of your body pushing on the ice via your skis lowers the snow’s melting point enough that you melting is occuring at a molecular level on contact, allowing you to slip and slide down the slopes. The same concept is applied to skating but at a much higher amount of pressure due to the pin point surface area of the blade. Once the pressure has passed, the
For solids which expand on melting (eg., paraffin wax, silver, gold, copper), increase in pressure increases the melting point i.e., pressure applied is directly proportional to melting point as increase inpressure opposes expansion.
30/09/2008 · The melting of ice under pressure is investigated with a series of first-principles molecular dynamics simulations. In particular, a two-phase approach is used to determine the melting temperature of the ice-VII phase in the range of 10–50 GPa.
pressure dependency is generally considered insignificant). Determining the MP is a simple and fast method used in many diverse areas of chemistry to obtain a first impression of the purity of a substance. This is because even small quantities of impurities change the melting point, or at least clearly enlarge its melting range. Melting point determinations are more than just a classroom
the effects of solutes and of pressure Freezing point depression is the lowering of the equilibrium freezing or melting temperature by solutes in the liquid phase.
Regelation effect of pressure on melting point ~ Science

Effect of Pressure on the Melting Point of Ice
1 AIM :. boiling tubes.To determine the effect of impurities on the freezing point of water. 2. If we add sugar or salt to this water its vapour pressure becomes lower and boiling point increases. 3) Put a mixture of ice and KNO3 in a beaker and fix test tube no. stirrer.2 and 2g of glucose to boiling tube no. when 1 mole of any non electrolyte is dissolved in 1 litre of water the elevation of
The melting point of a pure substance is always higher than the melting point of that substance when a small amount of an impurity is present. Pressure also affects the melting point of a substance. As the pressure on the substance increases, the melting point decreases.
Thus, the melting point of a normal solid is raised. Abnormal solids, like ice and bismuth, contract on melting into liquids. When pressure is applied on the surface …
at pressure P, Tm,1atm is the melting point at 1 atmosphere pressure, and a and b are regression constants. P tp can often be neglected because it is much smaller than P in value.
Melting point: The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. The melting point of water is dependent of the pressure above the ice (solid water), and the boiling temperature decreases with increasing pressure.
25/02/2012 · Experiment to illustrate the effect of pressure on the melting point The experiment illustrated in the image shows the effect of pressure on the melting point of ice in a rather striking manner. 1- A block of ice rests on two supports, and a thin …
Ice should be dry before using for melting point determination. The bulb of the thermometer should be dipped in ice and should be surrounded on all sides with ice. Maintain a uniform temperature, by continuous stirring.
Boiling water with ice: Effect of pressure on the boiling point of water. Brit Ofstedal, Kingsland High School, Spring Valley, MN Author Profile. Summary. In this activity, which is a discrepant event with guided inquiry, the teacher will go through the steps of boiling water with ice. Through the students telling and recording WHAT is happening, the teacher is showing the students what
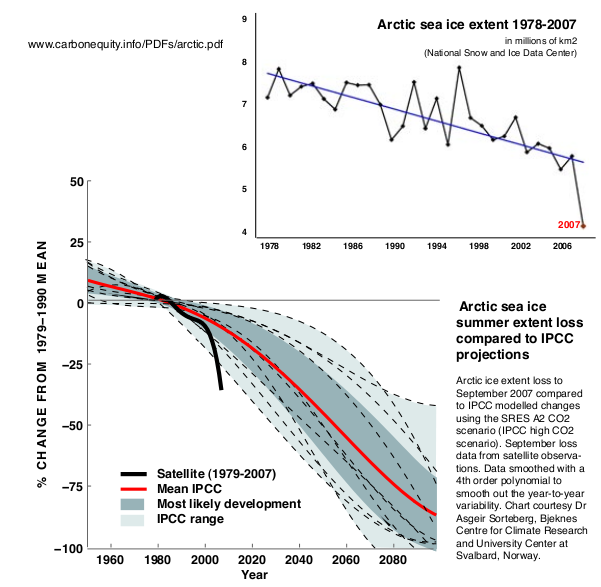
The effects of sea ice decline on the atmosphere can be divided into local and remote effects. Local effects are here defined as the effects that occur in regions that have during
Melting ice under pressure Sept. 23, 2008 Visualization by Eric Schwegler/LLNL A snapshot from a first-principle molecular dynamics simulation of ice-VII …

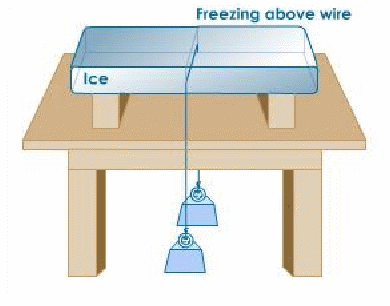
Effect of Pressure on Melting Point of Ice Description: Two weights connected by piano wire are hung on a bar of ice. The wire cuts through the bar of ice.
Yes, we all learned that the pressure from the skates melts a layer of water but that’s still pretty much false. the actual effect of that sort of pressure on ice scarcely lowers the melting point.
Therefore, since raises in pressure tend toward decreasing the volume of the two phases in equilibrium, the rise in pressure will favor the transition from ice to water, so that the melting will occur more readily and therefore the melting point will be shifted to a lower temperature.
It depends upon whether, when the solid melts, it either expands and so becomes less dense, or it contracts and becomes more dense. Most solids do the former, such that the solid is more dense than the liquid and therefore sinks within it. But, a
E.D. Waddington, C.S. Lingle, in Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences, 2015. Ice sheets can also slide over their substrates if the basal ice is at the pressure-melting temperature and if sufficient water is present, from basal melting, to lubricate the interface.
Abstract. The melting of ice under pressure is investigated with a series of first-principles molecular dynamics simulations. In particular, a two-phase approach is used to determine the melting temperature of the ice-VII phase in the range of 10–50 GPa.
The melting point is lowered with an increase in pressure. So, Ice melts at a temperature less than 0 Celsius. This phenomenon is also called regelation and is used in ice skating. When the skaters skate on ice, the increased pressure due to their…
This behaviour can pre- sumably be explained due to an enhanced pressure melting effect at higher normal stresses and temperatures close to 0 • C, leading to liquid formation along the rock-ice
Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation: the effects of solutes and of pressure Freezing point depression is the lowering of the equilibrium freezing or melting temperature by solutes in …
19/03/2012 · Hey, I have read that INCREASING the external pressure on solids INCREASES their melting point.(except for ice) WHY DOES THIS HAPPEN? (This is similar to the effect on Boiling point which rises when external pressure is increased.

20/09/2008 · when pressure is applied melting point of ice is lowered. one reason for increase in pressure is that when the temperature decreases pressure increases. so when pressure is applied on ice melting point of ice becomes becomes less than the actual melting point.similarly when the pressure decreases the result is vice-versa.
finally, if all the ice is at the pressure melting point, except in a surface layer during the winter, it is called temperate. Glaciers in Iceland are all temperate. Most of the glaciers in Svalbard are polythermal. The large ice-sheets, Greenland and Antarctica, are cold glaciers. 1 Thermal parameters Table 1 lists the main parameters needed for calculations of temperture. Table 1. Thermal
When ice melts into sea water the effect is to cool and freshen. Consider unit mass of water at temperature T 0, and salinity S 0 coming into contact with the base of an ice shelf where the in situ freezing point is T f.
The melting point depression of the pore ice revealed an almost linear relationship with ln(p 0 /p) of the capillary condensation pressure of nitrogen at 77 K for various pores of different sizes and shapes.
18/03/2017 · The melting points of compounds may be lower than the reported values because it may contain small amounts of the impurities or solvents. Impurities in a solid cause a melting point …
How does pressure affect the melting point of ice?
The first observation of pressure effect on the melting point was made by Perkins in 1826. He compressed acetic acid [CH 3 COOH] with 1100 Atm. pressure …
Revised Spring 2017 AMM Effect of Pressure on the Melting Point of Ice . Chemicals and Equipment Needed • d-H 2O • 2 short ring stands – J
Process Safety Beacon – Snow and Ice Hazards – they can cause more than slips and falls!
its lower surface to lower the melting point of its ice, allowing liquid water flow from the base of a glacier to lower elevations when the temperature of the air is above the freezing point of water.
Three factors that affect the rate at which ice melts are temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities. Objects melt when they have reached an appropriate temperature and pressure where they can transition from their solid phase to their liquid phase.
4) At room temperature (30°C) a student sets up an apparatus to determine the melting point of ice. The student takes a beaker half filled with ice and dips a mercury thermometer in it. – the maelstrom henry neff pdf Composition of Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate and the Effect of Pressure on the Decomposition1 S the hydrate and ice melting points appear to have been generally defined to better than lo and 100 bars. Considerably more accurate determination of the variation of hydrate decomposition temperature (and temp OC FIG. 1. Illustration of capacitance and volume changes at temperatures of phase changes
The melting points of compounds may be lower than the reported values because it may contain small amounts of the impurities or solvents. Impurities in a solid cause a melting point depression because the impurity disrupts the crystal lattice energies. For example if a compound had a melting point of 55-57 °C and an impurity was introduced which had a melting point of 112 °C , the melting
Conversely, substances which contract in volume on solidifying have their melting points raised by pressure. Thus, the freezing point of water is lowered Thus, the freezing point of water is lowered by just over 0.007 K per atmosphere increase in pressure, while the freezing point of paraffin increases by about 0.04 K per atmosphere.
The melting of ice under pressure is investigated with a series of first-principles molecular dynamics simulations. In particular, a two-phase approach is used to determine the melting temperature
hi, say any solid(except the ice) ,during melting its volume increases.thus if pressure is low it will help melting. but in the case of ice, as the water contracts on
In this case, if you increase the pressure on the ice the ice-water system wants to try to lower it again. It can do that by making itself fit into a smaller volume. But since water fills a smaller volume when it’s liquid, rather than solid, it will go to a lower melting point — allowing more solid to become liquid.
The Science: Applying pressure to ice has the effect of lowering its freezing point, which means it will melt to form liquid water above a certain temperature. However, the pressure exerted on the
Graphene2017 March 28-31, 2017 Barcelona (Spain) Pressure induced melting of graphene confined ice K. Sotthewes, P. Bampoulis, H.J.W. Zandvliet, D. Lohse and
OK, so what does this have to do with pressure and melting. Well, the answer is exactly the same as the above, only in reverse. If we take some ice and push on it hard by putting lots of pressure on it, we are really just trying to make it take up less space. One way for ice to take up less space is for it to turn back into water, which is the answer to your question.
An increase in atmospheric pressure raises the boiling point of a liquid by raising the vapor pressure of the water above the liquid. This increases the amount of thermal energy needed to increase the vapor pressure of the water to match, raising the boiling point.
Melting of ice under pressure mately linear, and at higher temperatures, an inflection point near 1,500 K can clearly be seen in the 50-GPa simulations. For the higher-pressure simulations, similar (although increasingly less pronounced) changes can be found at higher temperatures. Along the 50 GPa isobar, the MD run at 1,400 K was carried out twice: once by heating from the sample at
of ice at the pressure-melting point is increased rapidly, the temperature through the parcel of ice will fall rapidly to the new pressure-melting point, the necessary heat balance being preserved by absorption of latent heat by melting within the ice mass.
Regelation is the phenomenon of melting under pressure and freezing again when the pressure is reduced. Many sources [who?] state that regelation can be demonstrated by looping a fine wire around a block of ice, with a heavy weight attached to it.
Temperature distribution in glaciers University of Iceland
Basal Melting an overview ScienceDirect Topics

ice Why does an increase in pressure raise melting point
Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation the

Q & A How can pressure melt ice? Department of Physics
Effect of Frozen Storage Temperature on the Quality of


Theory Under Pressure Skates on Thin Ice HuffPost UK
CBSE Class 9 Science Practical Skills – Melting Point of
– Melting ice under pressure Lawrence Livermore National
Activity Title Causes and Effects of Melting Ice COSEE.net
What is the effect of air pressure on melting point of
Effect of Pore Shape on Freezing and Melting Temperatures
Effect of pressure on Melting point Physics Forums
Melting ice under pressure Lawrence Livermore National
pressure dependency is generally considered insignificant). Determining the MP is a simple and fast method used in many diverse areas of chemistry to obtain a first impression of the purity of a substance. This is because even small quantities of impurities change the melting point, or at least clearly enlarge its melting range. Melting point determinations are more than just a classroom
Melting of ice under pressure mately linear, and at higher temperatures, an inflection point near 1,500 K can clearly be seen in the 50-GPa simulations. For the higher-pressure simulations, similar (although increasingly less pronounced) changes can be found at higher temperatures. Along the 50 GPa isobar, the MD run at 1,400 K was carried out twice: once by heating from the sample at
Regelation is the phenomenon of melting under pressure and freezing again when the pressure is reduced. Many sources [who?] state that regelation can be demonstrated by looping a fine wire around a block of ice, with a heavy weight attached to it.
The melting point depression of the pore ice revealed an almost linear relationship with ln(p 0 /p) of the capillary condensation pressure of nitrogen at 77 K for various pores of different sizes and shapes.
To determine the effects of different substances such as road salt, calcium chloride, sand, kitty litter, calcium magnesium acetate and Safe Paw (a commercial eco-friendly product) on melting ice while protecting the lawn.
Freezing and Melting of Water The cooling and warming behavior of water is investigated. With the use of technology, water temperature data is collected, graphed and analyzed. The freezing and melting points of water are determined and compared. Hypothesis The freezing and melting points of a substance may be determined by observing the warming and cooling behavior of that substance. …
Cooling of sea-water to its pressure melting point by melting of ice at depth has two important results. The outflow of cold, dense Ice Shelf Water, produced by this mechanism, is a major source
Three factors that affect the rate at which ice melts are temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities. Objects melt when they have reached an appropriate temperature and pressure where they can transition from their solid phase to their liquid phase.
Thus, the melting point of a normal solid is raised. Abnormal solids, like ice and bismuth, contract on melting into liquids. When pressure is applied on the surface …
With a pressure change apply Le Châtelier’s principle – “If a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in pressure . . . . . . . then the equilibrium shifts in such a way so as to undo the effect …
This behaviour can pre- sumably be explained due to an enhanced pressure melting effect at higher normal stresses and temperatures close to 0 • C, leading to liquid formation along the rock-ice
It depends upon whether, when the solid melts, it either expands and so becomes less dense, or it contracts and becomes more dense. Most solids do the former, such that the solid is more dense than the liquid and therefore sinks within it. But, a
In this case, if you increase the pressure on the ice the ice-water system wants to try to lower it again. It can do that by making itself fit into a smaller volume. But since water fills a smaller volume when it’s liquid, rather than solid, it will go to a lower melting point — allowing more solid to become liquid.
Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation: the effects of solutes and of pressure Freezing point depression is the lowering of the equilibrium freezing or melting temperature by solutes in …
Freezing point depression and boiling point elevation: the effects of solutes and of pressure Freezing point depression is the lowering of the equilibrium freezing or melting temperature by solutes in …
Pressure induced melting of graphene confined ice
Compression shortens the OH nonbond and lengthens the H-O
Composition of Tetrahydrofuran Hydrate and the Effect of Pressure on the Decomposition1 S the hydrate and ice melting points appear to have been generally defined to better than lo and 100 bars. Considerably more accurate determination of the variation of hydrate decomposition temperature (and temp OC FIG. 1. Illustration of capacitance and volume changes at temperatures of phase changes
Ice Melting Point Validation Method for Digital Data
(PDF) Melting of ice under pressure ResearchGate
Melting of ice under pressure mately linear, and at higher temperatures, an inflection point near 1,500 K can clearly be seen in the 50-GPa simulations. For the higher-pressure simulations, similar (although increasingly less pronounced) changes can be found at higher temperatures. Along the 50 GPa isobar, the MD run at 1,400 K was carried out twice: once by heating from the sample at
Melting ice under pressure Lawrence Livermore National
Melting of ice under pressure PNAS
effect of pressure on melting point of ice? Yahoo Answers
of ice at the pressure-melting point is increased rapidly, the temperature through the parcel of ice will fall rapidly to the new pressure-melting point, the necessary heat balance being preserved by absorption of latent heat by melting within the ice mass.
Effect of Pressure on Melting Point of Ice
OK, so what does this have to do with pressure and melting. Well, the answer is exactly the same as the above, only in reverse. If we take some ice and push on it hard by putting lots of pressure on it, we are really just trying to make it take up less space. One way for ice to take up less space is for it to turn back into water, which is the answer to your question.
Q & A pressure and melting ice Department of Physics
Effect of Frozen Storage Temperature on the Quality of
Effect of Impurities on The Solution Melting Point
19/03/2012 · Hey, I have read that INCREASING the external pressure on solids INCREASES their melting point.(except for ice) WHY DOES THIS HAPPEN? (This is similar to the effect on Boiling point which rises when external pressure is increased.
(PDF) Melting of ice under pressure ResearchGate
When ice melts into sea water the effect is to cool and freshen. Consider unit mass of water at temperature T 0, and salinity S 0 coming into contact with the base of an ice shelf where the in situ freezing point is T f.
Dissociation Termination of Methane–Ethane Hydrates in
Plastic Flow and Pressure Melting in the Deformation of Ice I
What is the effect of pressure on the melting point of solids?
Melting point: The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. The melting point of water is dependent of the pressure above the ice (solid water), and the boiling temperature decreases with increasing pressure.
Melting Point of Ice (Theory) Class 9 Chemistry